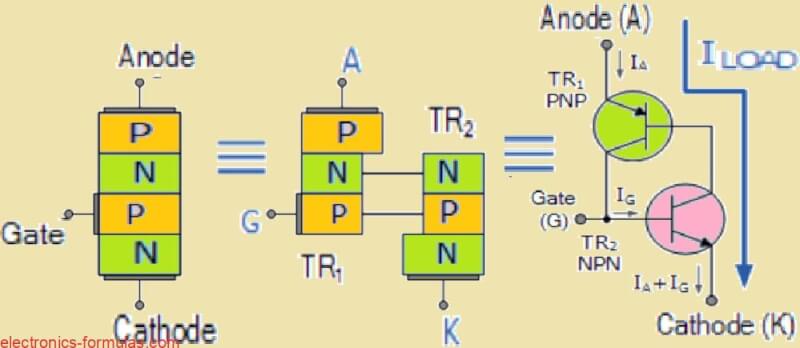
Now in this tutorial we are going to learn in deep about one very important power electronic device called thyristor or also called Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR). We will try to understand how it is built and how it works. This thyristor is kind of similar to a transistor but still it is different in […]
Explained: 7-Segment Display Counter Circuits
In today’s world showing numbers and letters on multiple LED displays is pretty simple, thanks to microcontrollers like Arduino or Raspberry Pi. With just a small piece of code we can easily display the digits we need. But as electronics students or hobbyists there are times when we need to show multiple numbers or digits […]
Understanding MOD Counters or Cascaded Counter Circuits
A counter mainly works by adding one to its value every time it gets a pulse from the clock signal. When a counter counts up in response to the clock, we say it is in “count-up” mode. If it counts down instead, we call that “count-down” mode. There are also special counters that can do […]
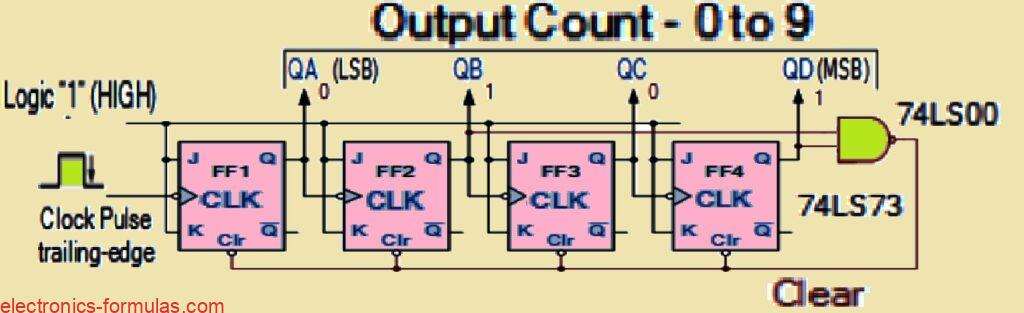
Understanding Various BCD Counter Circuits
We know that toggle T-type flip-flops can work as standalone divide-by-two counters. By connecting several toggle flip-flops in a sequence, we can create a digital Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) counter. This counter can store or display the frequency of a specific counting sequence. Clocked T-type flip-flops act as binary divide-by-two counters. In asynchronous counters, the output […]
How Bidirectional Counters Work
A bidirectional counter is a synchronous binary counter that can count both up and down. We can use it to count towards a specific value or back to zero. We can count upwards from zero to a preset value. Sometimes we also need to count down from a defined value to zero. This feature allows […]
Understanding Synchronous Counter Circuits
In asynchronous counters we find the output of one stage connects directly to the clock input of the next stage. This setup causes a problem called “Propagation Delay.” Here the timing signal is delayed slightly as it passes through each flip-flop. In contrast synchronous counters have all their stages clocked together at the same time. […]