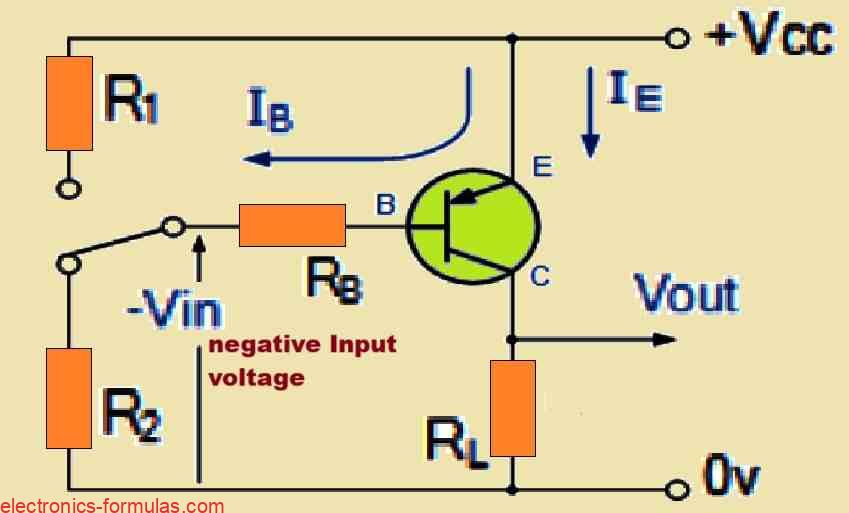
In applications where we use a transistor or a BJT to amplify an AC signal, it becomes crucial to set its base bias voltage correctly. This allows the transistor to sit comfortably in its “active” zone, which means we are working within the linear range of the output characteristic curves. The exciting part is that […]
Transistors
How PNP Transistors (BJTs) Work
When we talk of PNP BJTs, they are essentially the reverse of NPN transistors in structure. Instead of having two diodes alligned in the same direction, PNP transistors have them flipped around. This forms a Positive-Negative-Positive (PNP) configuration. If you look at the symbol for a PNP transistor, you will notice that there is an […]
How NPN Transistors (BJTs) Work: Explained with Calculations
In the previous tutorial we took a good look at the standard Bipolar Junction Transistors, which is often referred to as the BJT. We learned that it actually comes in two main types which are known as the NPN configuration, standing for Negative-Positive-Negative, and the PNP configuration which means Positive-Negative-Positive. So basically we have two […]
Explained: Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) and Configurations
If we look at the diodes, their internal construction look fairly straightforward. They are internally built using two sections of semiconductor material, forming what is called a PN-junction. But when we talk about a bipolar junction transistor or a BJT, things get a little more advanced. It involves adding an extra layer of semiconductor material […]