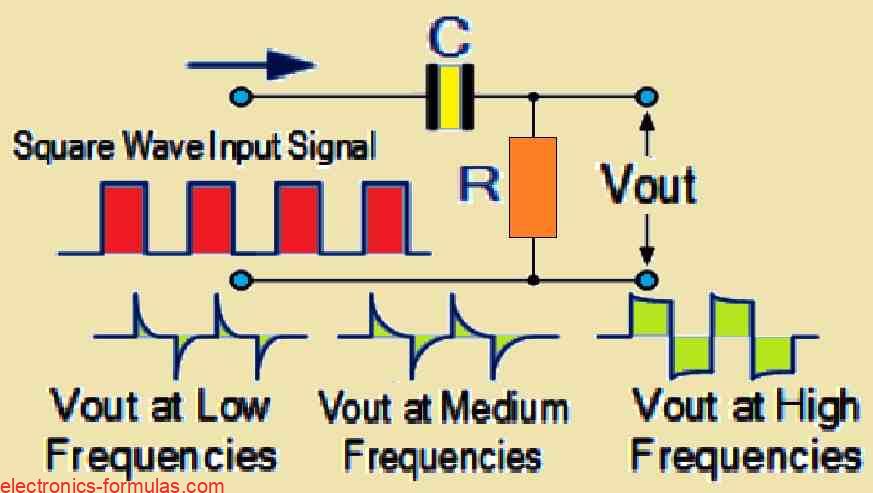
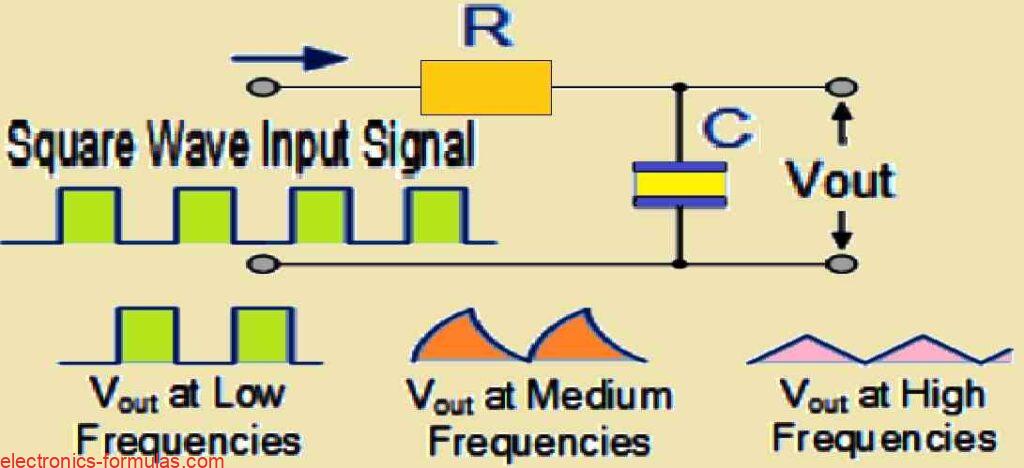
As we already know, a low-pass filter selectively permits signals with frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency fc to pass through. This shows that although the high-frequency elements of the input signal are attenuated (weakened), the lower-frequency elements are retained in the output. A passive high-pass filter, on the other hand, functions in the opposite […]
Learning Passive Low Pass Filter Circuit Calculations
Basically passive RC filters are circuits that separate various frequencies within a signal. We can consider a signal as a collection of distinct-pitched noises. We can make an RC filter to only allow high-pitched sounds to pass through (such as a treble filter) or only the low-pitched sounds to pass through (similar to a bass […]
Understanding Capacitive Reactance with Formulas
Capacitors have a special way of opposing alternating current (AC) which is called capacitive reactance. This is like an internal resistance in the capacitor which changes based on the frequency of the electricity flowing through it. Unlike normal resistance which stays the same, no matter how fast the electricity changes (frequency), capacitive reactance is affected […]