In this post, we are talking about amplifiers and filters. These are two very common types of electronic circuits that we use a lot. Now if we see how they work then we can say that amplifiers do amplification and filters do filtration. That is why we call them that. Amplifiers and Filters Together But […]
Understanding Input Impedance of a BJT Amplifier Circuit
The Input Impedance ZIN, or what people call as the Input Resistance, is important thing when making transistor amplifier circuits. It helps us to tell what kind of amplifier it is by looking at input and output impedance and also power and current ratings. Now amplifier impedance value is very important for circuit analysis, especially […]
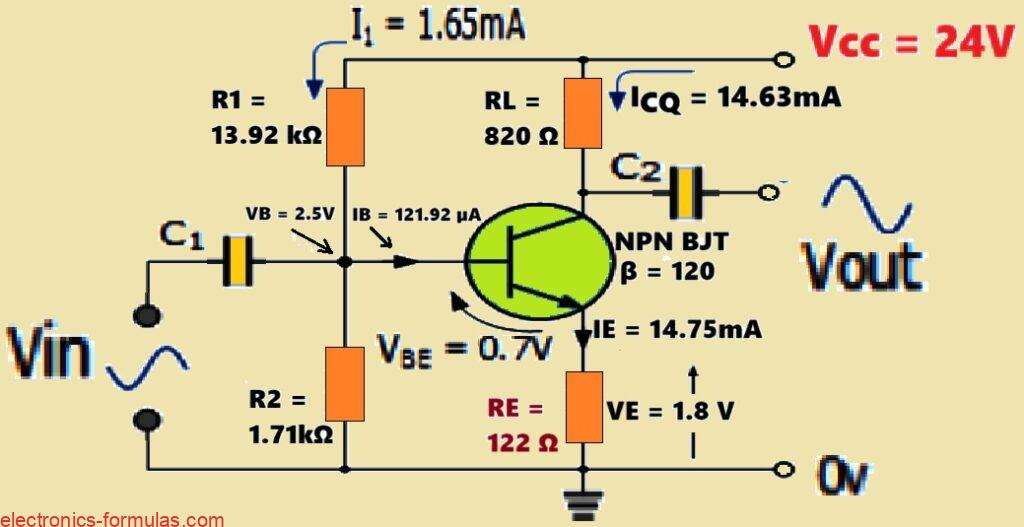
Summarizing Audio Amplifier Circuit Characteristics
So when we think about amplifiers we usually picture those audio amplifiers that we come across in our stereos, CD players and radios which we have set up in our homes. In this part where we are investigating amplifiers, we took a closer look at just one type of amplifier circuit, specifically the single bipolar […]
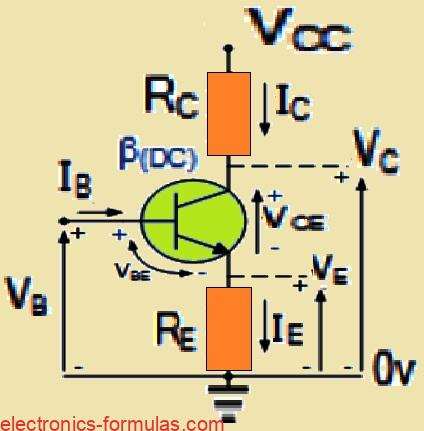
How to do Transistor Biasing Correctly
If you want to keep a bipolar transistor running smoothly, it really comes down to getting the right balance of its base current, collector voltage, and collector current. So if we want to use a transistor as a linear amplifier, we have got to bias it properly. Biasing basically means setting it up so it […]
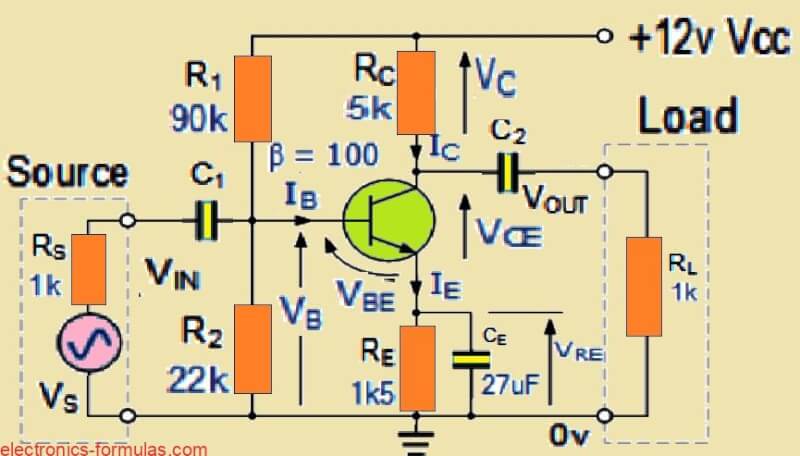
Why We Use Emitter Resistor in a BJT Amplifier Circuit
The goal of any BJT amplifier is to keep the DC biased input voltage steady and to make the AC signal bigger. To do this we use something called an “emitter resistance” that connects to the emitter part of a transistor. This helps the amplifier stay stable with its bias. The stability happens because the […]
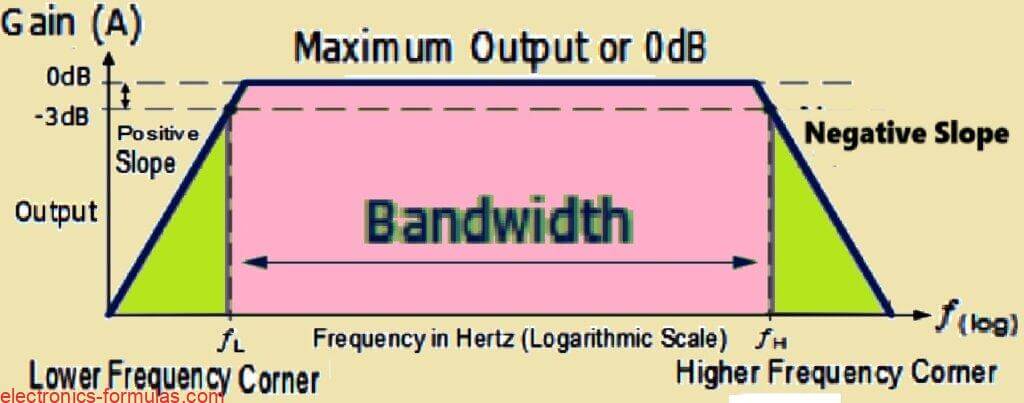
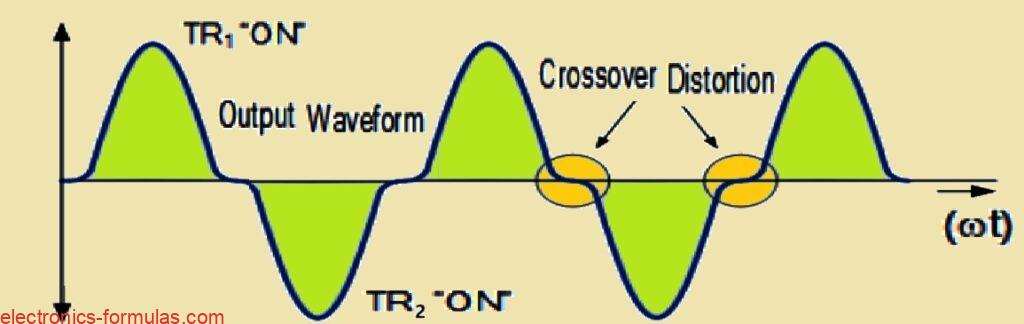
What is Crossover Distortion in Class-B Amplifier Circuits
When we talk about distortion in an amplifier we are basically referring to how the output signal does not exactly match the original input signal it gets altered in some way. One particular type of distortion that affects amplifiers with a push-pull design is something known as crossover distortion. This happens specifically at the point […]