In today’s world showing numbers and letters on multiple LED displays is pretty simple, thanks to microcontrollers like Arduino or Raspberry Pi. With just a small piece of code we can easily display the digits we need. But as electronics students or hobbyists there are times when we need to show multiple numbers or digits […]
Understanding MOD Counters or Cascaded Counter Circuits
A counter mainly works by adding one to its value every time it gets a pulse from the clock signal. When a counter counts up in response to the clock, we say it is in “count-up” mode. If it counts down instead, we call that “count-down” mode. There are also special counters that can do […]
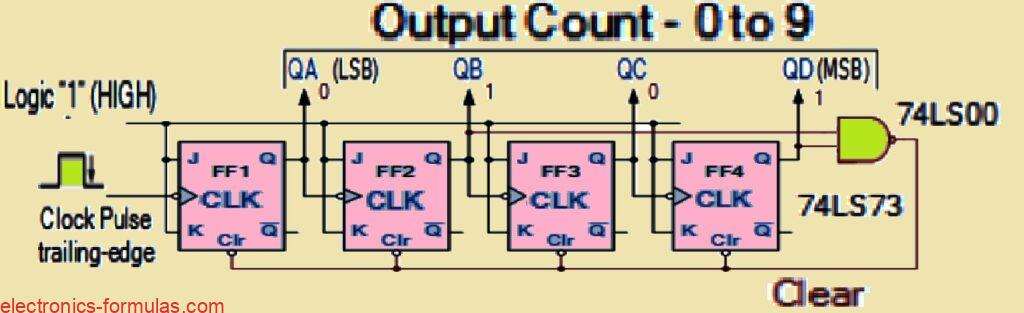
Understanding Various BCD Counter Circuits
We know that toggle T-type flip-flops can work as standalone divide-by-two counters. By connecting several toggle flip-flops in a sequence, we can create a digital Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) counter. This counter can store or display the frequency of a specific counting sequence. Clocked T-type flip-flops act as binary divide-by-two counters. In asynchronous counters, the output […]
How Bidirectional Counters Work
A bidirectional counter is a synchronous binary counter that can count both up and down. We can use it to count towards a specific value or back to zero. We can count upwards from zero to a preset value. Sometimes we also need to count down from a defined value to zero. This feature allows […]
Understanding Synchronous Counter Circuits
In asynchronous counters we find the output of one stage connects directly to the clock input of the next stage. This setup causes a problem called “Propagation Delay.” Here the timing signal is delayed slightly as it passes through each flip-flop. In contrast synchronous counters have all their stages clocked together at the same time. […]
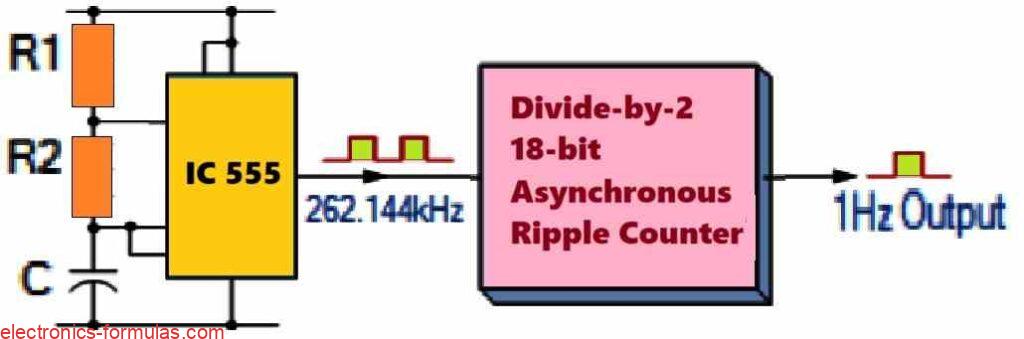
Explained: How Asynchronous Counter Works
An asynchronous counter is really cool because it can handle a total of 2n-1 different counting states. For example a 4-bit counter set up as MOD-16 can count from 0 all the way to 15, making it great for things like frequency division. But you can also use the basic design of an asynchronous counter […]