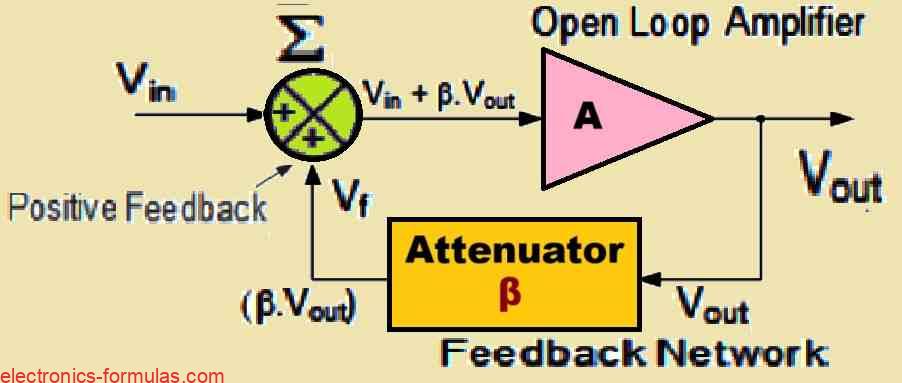
In the RC Oscillator tutorial, we saw that by connecting resistors and capacitors together with an inverting amplifier we can create an oscillating circuit. One of the simplest ways to generate a sine wave is through a circuit known as the Wien Bridge Oscillator. This oscillator replaces the traditional LC (inductor-capacitor) tuned tank circuit with […]
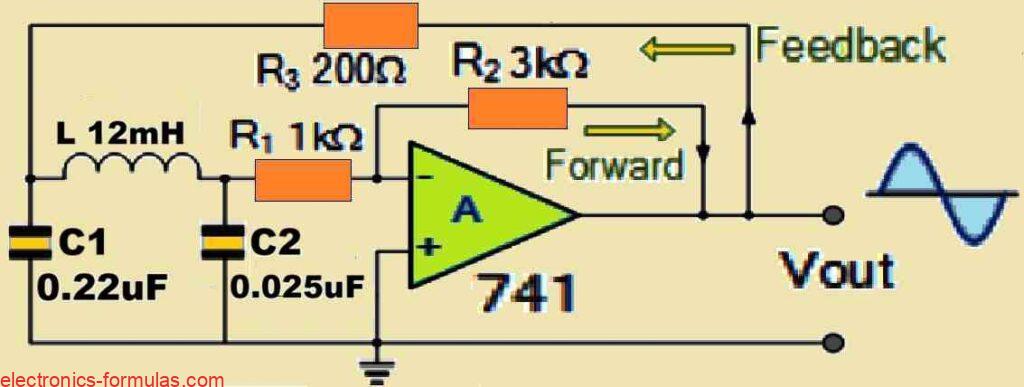
Understanding RC Oscillator Circuit, with Formulas
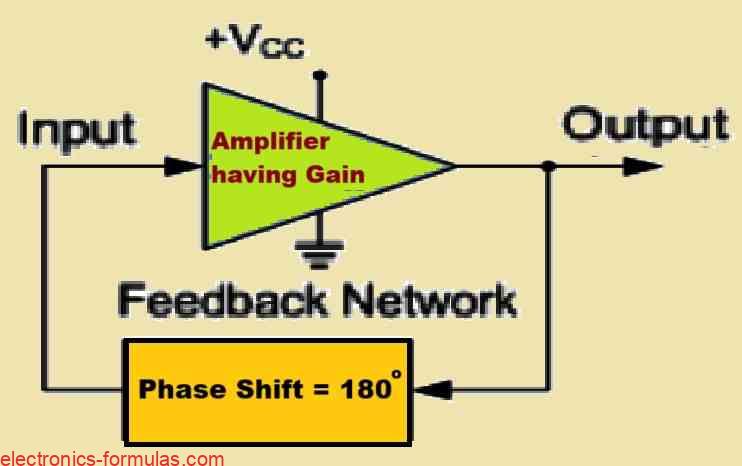
We all known that a single-stage transistor amplifier, when built as a common-emitter amplifier, may initiate a 180-degree phase shift between its output and input signals. This built-in characteristic of the amplifier design could be used to build an effective RC oscillator circuit. Interestingly it may be possible for us to construct transistor stages to […]
Colpitts Oscillator Working, Explained with Calculations
Compared to the Hartley oscillator that we looked at in the last lesson, the Colpitts oscillator represents a very different way of designing tuned tank circuits. Similar to the Hartley oscillator which creates a sinusoidal output waveform by implementing an LC resonance sub-circuit between the collector and base of a single-stage transistor (BJT) amplifier, the […]
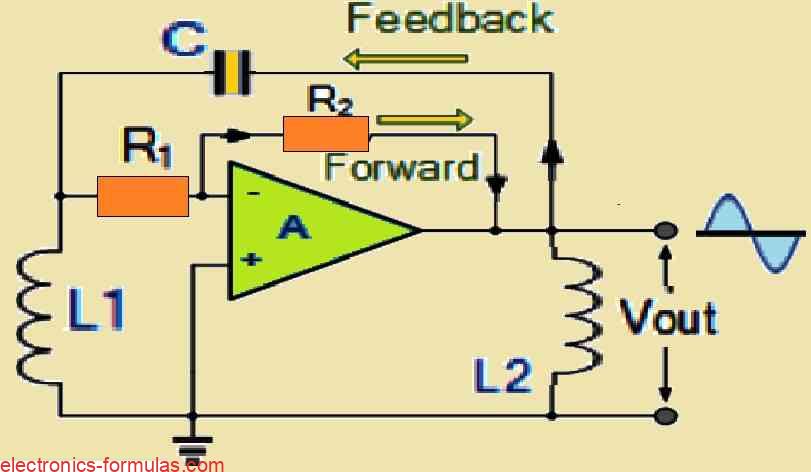
Understanding Hartley Oscillator Circuit, with Calculations
The basic LC Oscillator tank circuit that we discussed in one of our earlier posts has a significant limitation: it cannot alter the magnitude of its output oscillations. This means that the oscillations might be either too large or too little, making it difficult to get the desired results. It might also be difficult for […]
LC Oscillator Circuits: Explained with Calculations
An LC oscillator is a circuit which we can use to transform a direct current (DC) supply voltage into an alternating current (AC) output waveform. This output can exhibit various types of waveform shapes and frequencies which might range from complex forms to simple pure sine waves depending on the specific application requirements. These oscillators […]
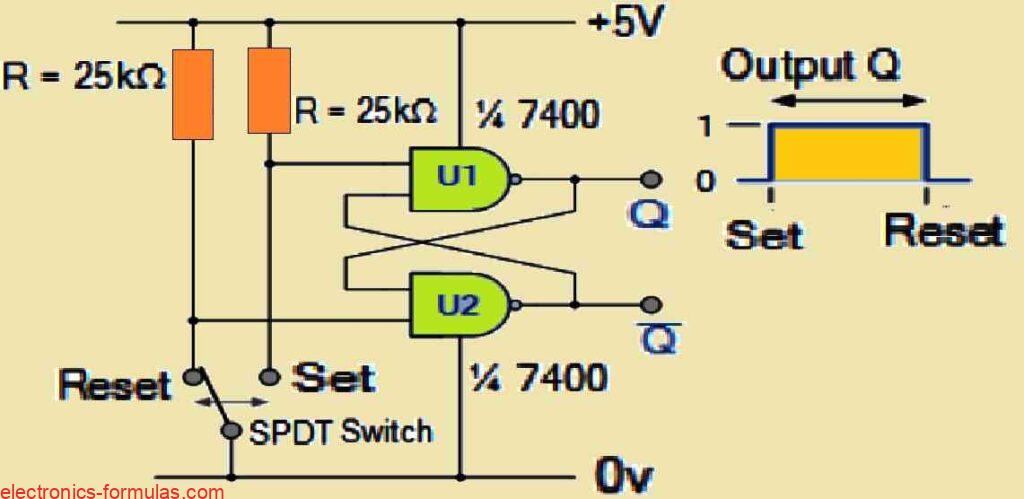
Pull-up Resistors and Pull-down Resistors: How to Calculate
In my practical works, when connecting digital logic gates to external circuits or devices, I personally ensure that their inputs and outputs are properly set to provide the correct switching conditions. This is where Pull-up Resistors come into play, because they help make sure that the inputs or outputs are functioning as per the expectations. […]