A digital buffer works in the same way like the NOT gate but with a distinct function. Although we find that a NOT gate (or inverter) generates an output which is just the inverse of its input, meaning that if we supply the input with a “HIGH” logic, then its output turns logic “LOW,” and […]
A Detailed Tutorial on Exclusive-NOR Gate
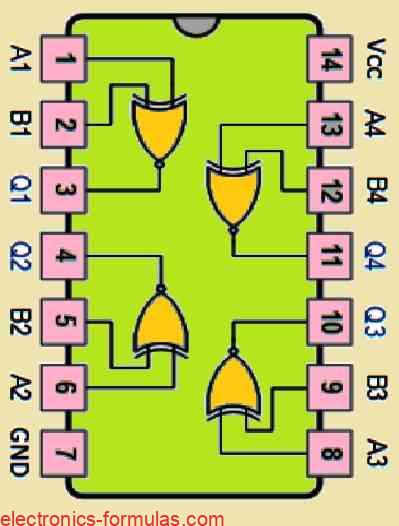
An “Exclusive-NOR Gate” will work by combining the functionality of an Exclusive-OR (XOR) gate and a NOT gate, but you will find that its truth table looks similar to that of a standard NOR gate, because, as we see that its output is typically at logic level “1” and switches to logic level “0” whenever […]
Understanding Exclusive-OR Gate: Tutorial
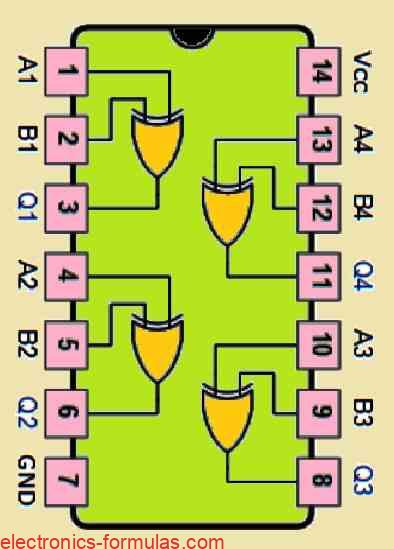
The Exclusive OR (XOR) Gate is a specialized type of digital logic gate that are widely utilized in digital arithmetic operations. Using these gates it becomes possible for us to calculate the sum of two binary numbers and we can also use these gates in error-detection and correction systems. So far in our logic gate […]
Understanding Logic NOR Gate: Tutorial
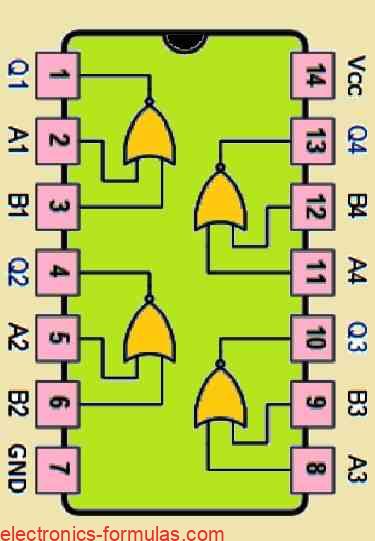
The term “inclusive” in “inclusive NOR” simply tells us that it is an alternative way of referring to a regular NOR gate. Like a standard NOR gate, the inclusive NOR gate gives us a logic “1” (high) output when all its inputs are at logic “0” and we get an output logic “0” (low) when […]
How Logic NAND Gate Works: Tutorial
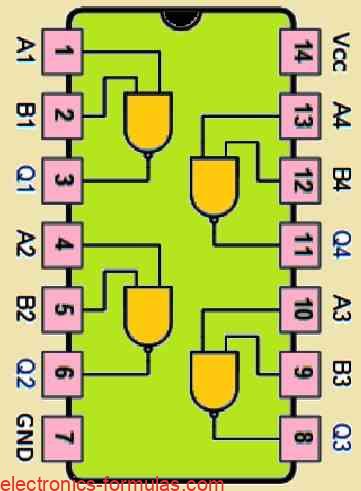
The NAND (Not-AND) gate is a fundamental digital logic gate which is designed to operate using a combination of an AND gate followed by a NOT gate. This means that the output of a NAND gate is generally at a logic level “1” (high) except in one specific case wherein it only switches to a […]
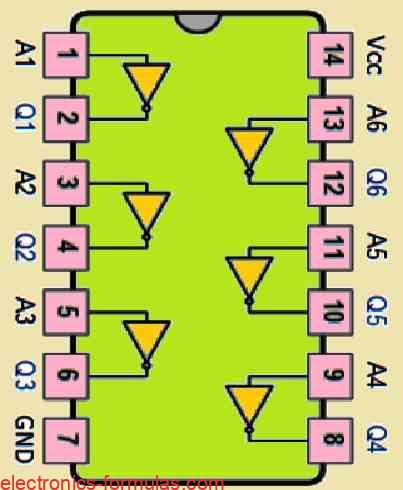
Understanding the Logic NOT Gate: Tutorial
A NOT gate which is also known as an inverter, is a digital logic component with a single input and a single output. The basic function of a NOT gate is to invert the input signal to generate an exactly opposite signal at its output. For example, suppose if we apply input of a NOT […]