Resistors in AC circuits are the only components that truly consume power (as heat), unlike reactances (capacitors and inductors) which just store and release it. Resistors convert electrical energy into heat (they dissipate energy), but inductors and capacitors store and release energy throughout the AC cycle, meaning they don’t actually consume power overall. In contrast […]
AC
Calculating Passive Components in AC Circuits
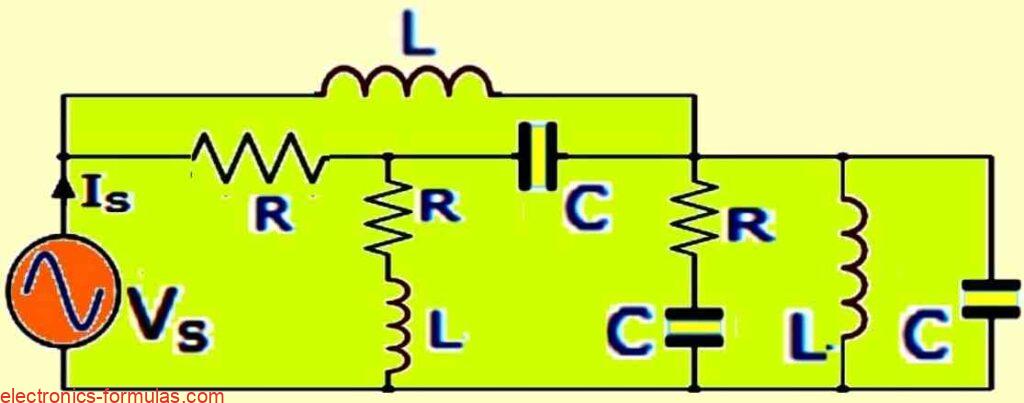
Passive components control or limit electrical signals, but can’t amplify them. Meaning, they can affect the signal in various ways, but not boost its power. In an electrical circuit we connect various parts to create a closed loop where electricity can flow. Three key parts that are involved are resistors, capacitors, and inductors. These are all […]
Calculating Harmonics in AC Circuits
Lets imagine a smooth alternating wave, harmonics are like ripples on top of that wave, making it look messy and uneven. These ripples are higher pitched sounds that mess with the original sound. Forget perfect sine waves….. In real circuits, many devices don’t play by the ideal rules. These are called non-linear devices. Because they’ […]
Calculating Reactive Power in AC Circuits
Reactive power (Q) is the oscillating energy exchange in AC circuits due to inductors and capacitors, which does not contribute to real power (P). When the circuit is a DC circuit, we can quickly multiply volts by amps to get watts of power used. This is true to purely resistive AC circuits as well. But […]
How to Calculate an AC Waveform
In this post we are going to discuss about how AC waveform works in circuit theory and we also see some main formulas which we can use to calculate different AC waveform values. Difference Between AC Waveform and DC Waveform So first we must understand that AC and DC are totally different. In electronics we […]