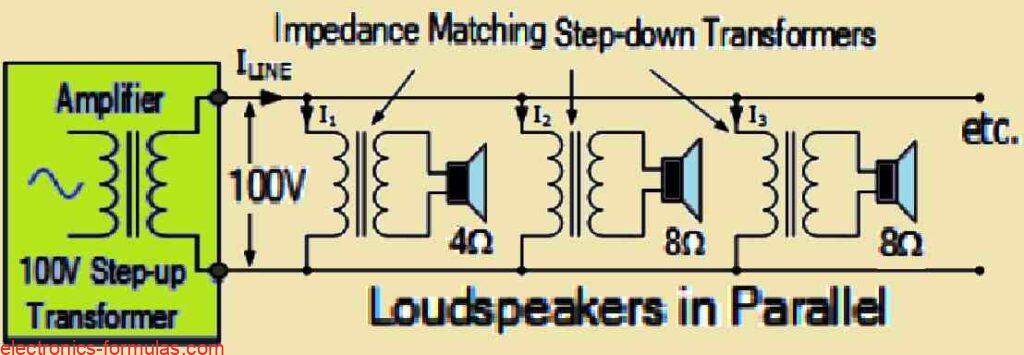
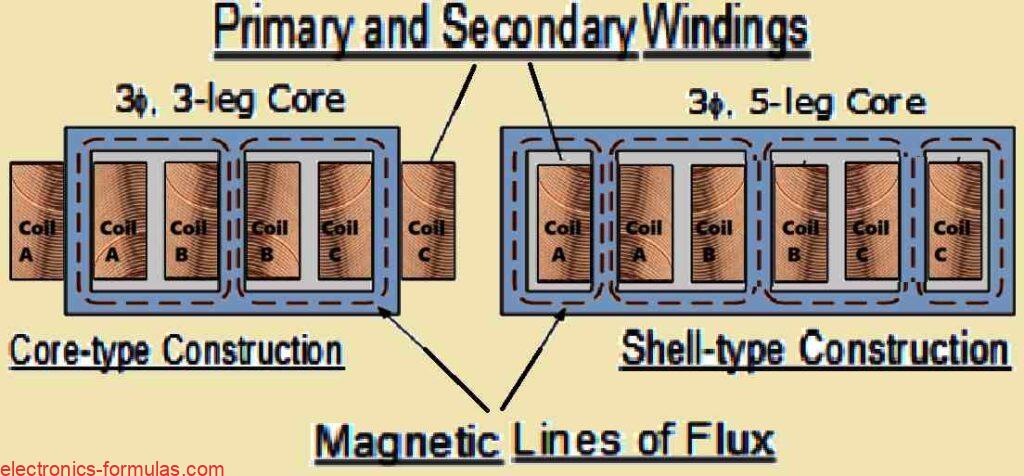
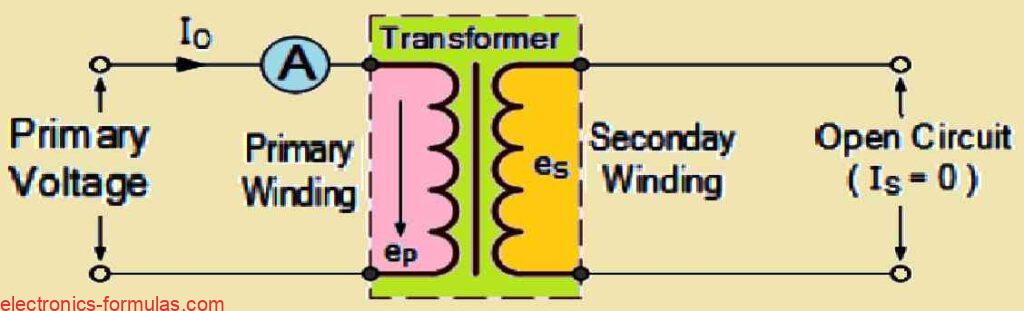
Transformers are really cool devices, that do more than just change the voltage of signals. One of their awesome features is called isolation. This means that there is no direct electrical link between the primary and secondary coils, which keeps the input and output circuits completely separate. This isolation is super useful in audio transformers […]
Calculations
Explained: Three Phase Transformers and Calculations
A 3-Phase electricity is basically a method we use to create and send electric power over really long distances so that our offices and industries can use it. In this setup we deal with three-phase voltages and currents which we can adjust either increase or decrease, using three-phase transformers. These transformers are pretty cool because […]
Current Transformer Explained with Calculations
We use a Current Transformer (C.T.) as an “instrument transformer.” It creates an alternating current in its secondary winding that matches the current in its primary winding. Current transformers lower high voltage currents to safer levels. They help us monitor the actual electrical current in an AC transmission line using a standard ammeter. The way […]
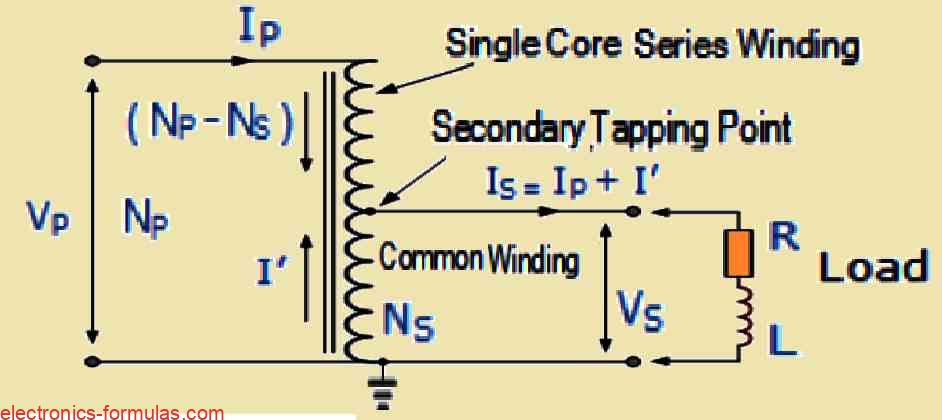
Autotransformer Working and Calculations Explained
An autotransformer is not like the traditional voltage transformer. Normally a voltage transformer has two distinct windings. These windings are called the primary and the secondary. But with an autotransformer things are a bit different because it only has one single winding that actually does the job of both the primary and the secondary. Now […]
Understanding Loading of Transformer with Calculations
In the earlier lessons we had about transformers, we kind of assumed that these devices were flawless. This means we thought their windings did not experience any core losses or copper losses at all. But when we actually use a transformer “on-load” we have to face the reality that there are always going to be […]
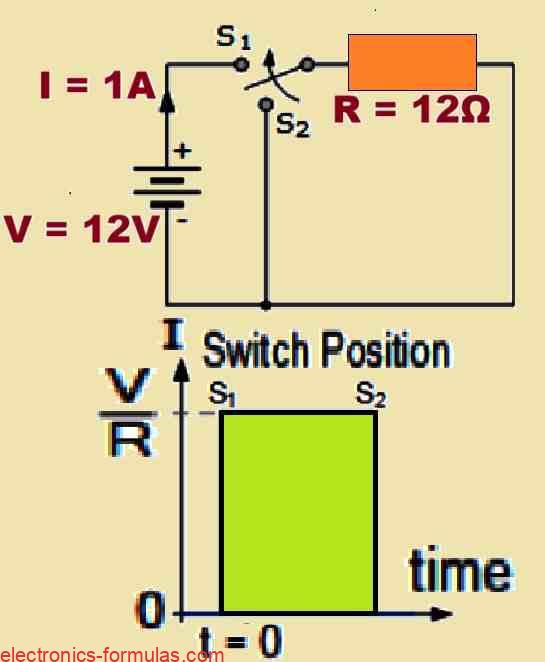
Time Constant Tau (τ): Explained with Calculations
In this post I will explain you the concept of Tau, or τ, which is the Greek letter we often see in electrical and electronic calculations. It represents what we call the “time constant” of a circuit which is basically a measure of how the circuit behaves over time. Now, when we talk about a […]