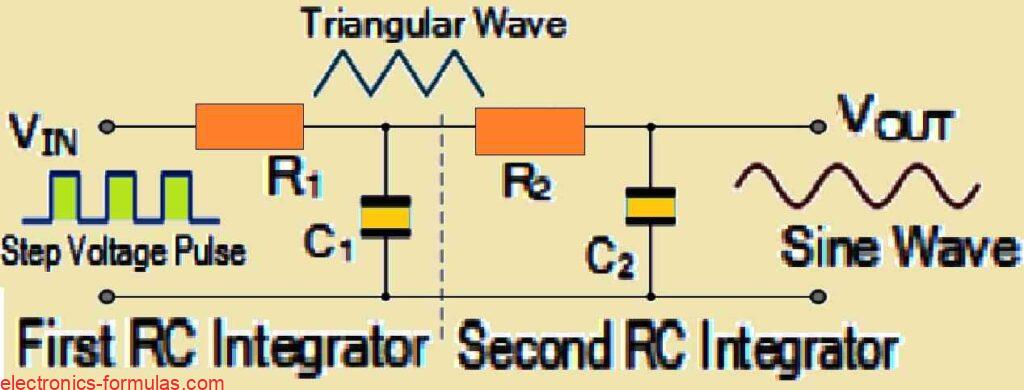
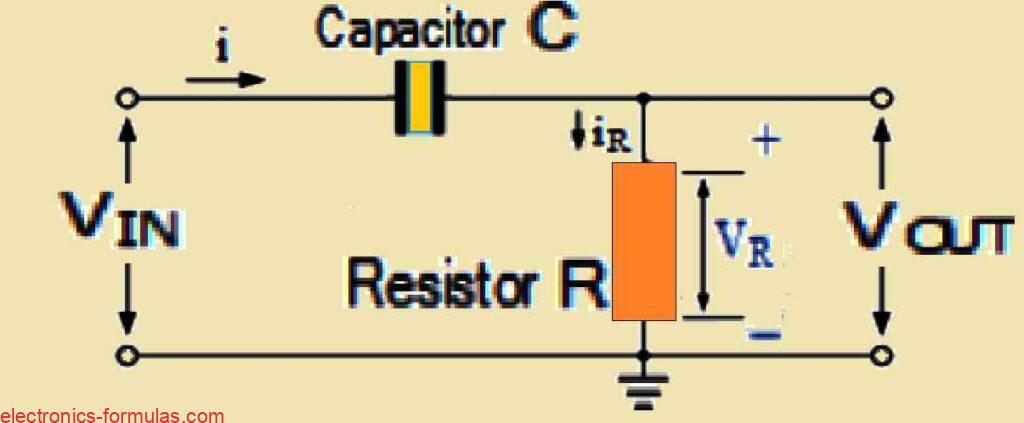
In a passive RC integrator circuit, we see that the input is actually connected to a resistor, while the output voltage is measured across the capacitor. This setup is basically the complete opposite of what goes on in an RC differentiator circuit. In RC integrator, when we make input signal high, the capacitor then starts […]
Calculations
Analyzing Passive RC Differentiator Circuit with Calculations
The passive RC differentiator is just a simple RC circuit where the resistor and capacitor are hooked up in series. What this does is give you an output signal that works like the mathematical process of differentiation. Basically, here the output shows how fast the input signal is changing at any given instant. In a […]
RC Time Constant Circuit Explained with Calculations
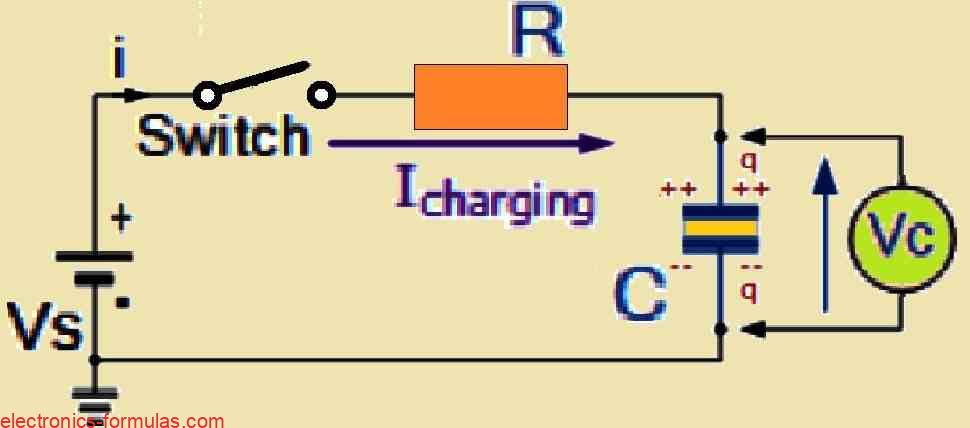
When we talk about charging a capacitor it is not something that can happen instantly. This is because capacitors have specific current-voltage i-v characteristics that shift depending on time. If you connect a resistor R and a capacitor C together into a circuit, you will get what is called an RC charging circuit. This setup […]
Twin-T Oscillator Circuit: From Calculations to Practical Applications
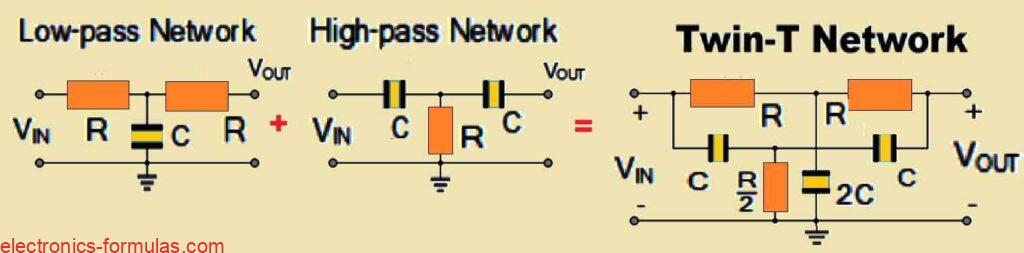
I have personally used the Twin-T RC oscillators a lot and I find it very interesting, mainly because it is designed to generate a sinewave output. It is ideal for fixed-frequency applications much like the Wien-bridge oscillator. The name “Twin-T” oscillator comes from the fact that it employs two “Tee”-shaped RC networks in the feedback […]
Understanding Quartz Crystal Oscillator Circuits, with Calculations
Quartz crystal oscillators allow us to overcome a number of issues that may have a substantial impact on the frequency stability of an oscillator circuit. These influences include, but are not restricted to, temperature variations, fluctuations in the load connected to the oscillator, and even changes in the DC power supply voltage. All of these […]
Wien Bridge Oscillator Circuit Explained with Calculations
In the RC Oscillator tutorial, we saw that by connecting resistors and capacitors together with an inverting amplifier we can create an oscillating circuit. One of the simplest ways to generate a sine wave is through a circuit known as the Wien Bridge Oscillator. This oscillator replaces the traditional LC (inductor-capacitor) tuned tank circuit with […]