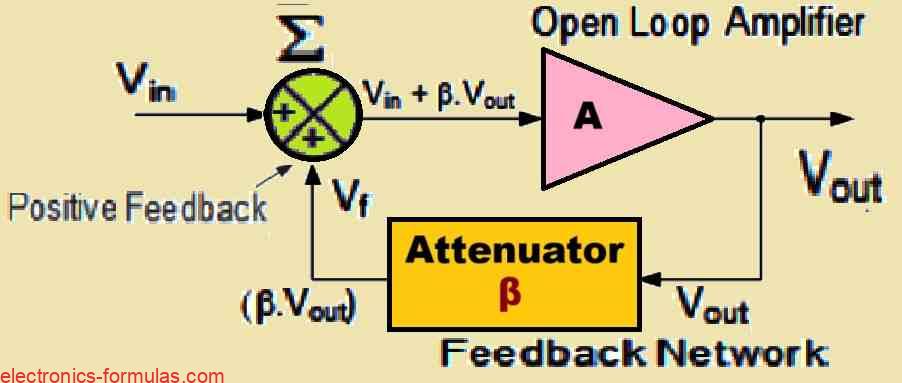
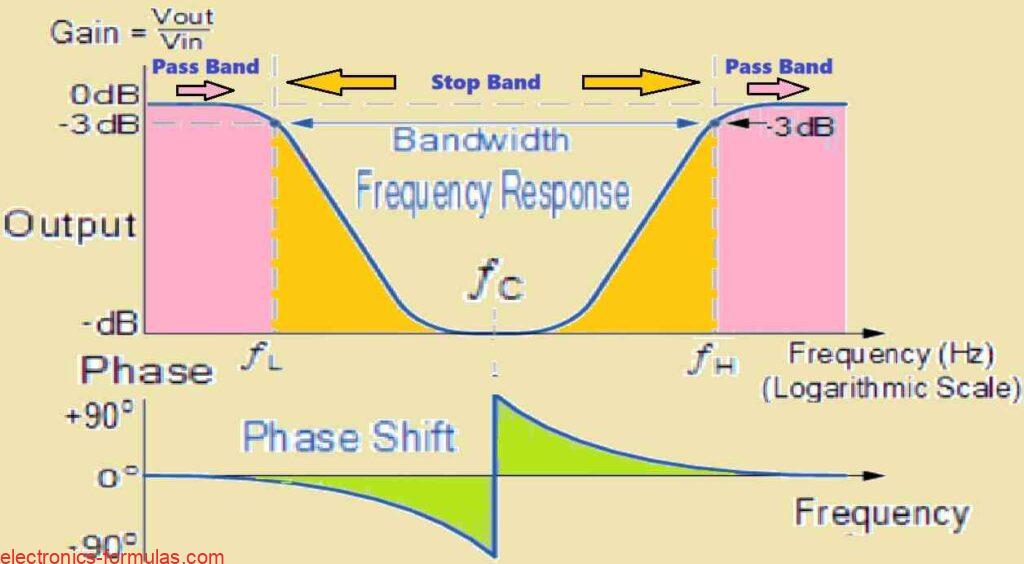
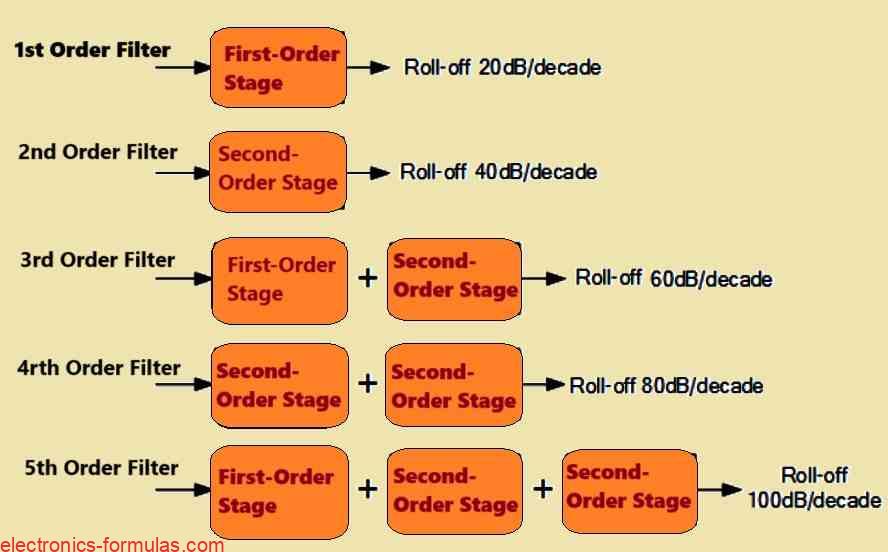
An LC oscillator is a circuit which we can use to transform a direct current (DC) supply voltage into an alternating current (AC) output waveform. This output can exhibit various types of waveform shapes and frequencies which might range from complex forms to simple pure sine waves depending on the specific application requirements. These oscillators […]
Explained
Band Stop Filter Circuit: Explained with Formulas
Another name for a band Stop Filter is the Notch Filter, which is designed to block and reject all frequencies that fall between its two cut-off frequency points, however all frequencies that are on the outer sides of this range, are allowed to pass through. A straightforward band-pass filter is created when we combine a simple […]
Active High Pass Filter Circuits Explained with Calculations
Although the fundamental filtering mechanism continues to be the same as in the passive RC filter, the active high-pass filter (HPF) integrates an operational amplifier (op-amp) to provide some essential characteristics. Gain & Control: The op-amp amplifies and controls the gain response of the filter. This is a huge benefit over passive high-pass filters, which […]